By Liu Liangliang

Neuropsychiatric disorders (NDs) are a collective name for a number of neurological diseases of the brain. The core symptom is cognitive dysfunction. In the past decade, a large number of studies have proved that there are certain relations between structural brain changes and cognitive impairment in ND patients. However, the existing methods only use shallow models to fuse the simple relations between multiple sources and ignore the complex interactions between brain structures and functional regions.
The biomedical imaging research team from College of Information and Management Science has made important progress in NDs classification. By studying the relationship between brain structural images (sMRI) and functional images (fMRI), the team proposed an enhanced multi-modal graph convolutional network (MME-GCN) in a binary classification between patients with an ND and healthy controls, based on a fusion of the structural and functional graphs of the brain (Figure 1). First, based on the same brain atlas, we constructed structural and functional graphs from sMRI and fMRI, respectively. Second, we used machine learning to extract important features from the structural graph network. Third, we used these extracted features to adjust the corresponding edge weights in the functional graph network. Finally, we trained a multi-layer GCN and used it in classification. MME-GCN achieved 93.71% classification accuracy on the open data set provided by the Consortium for Neuropsychiatric Physics.
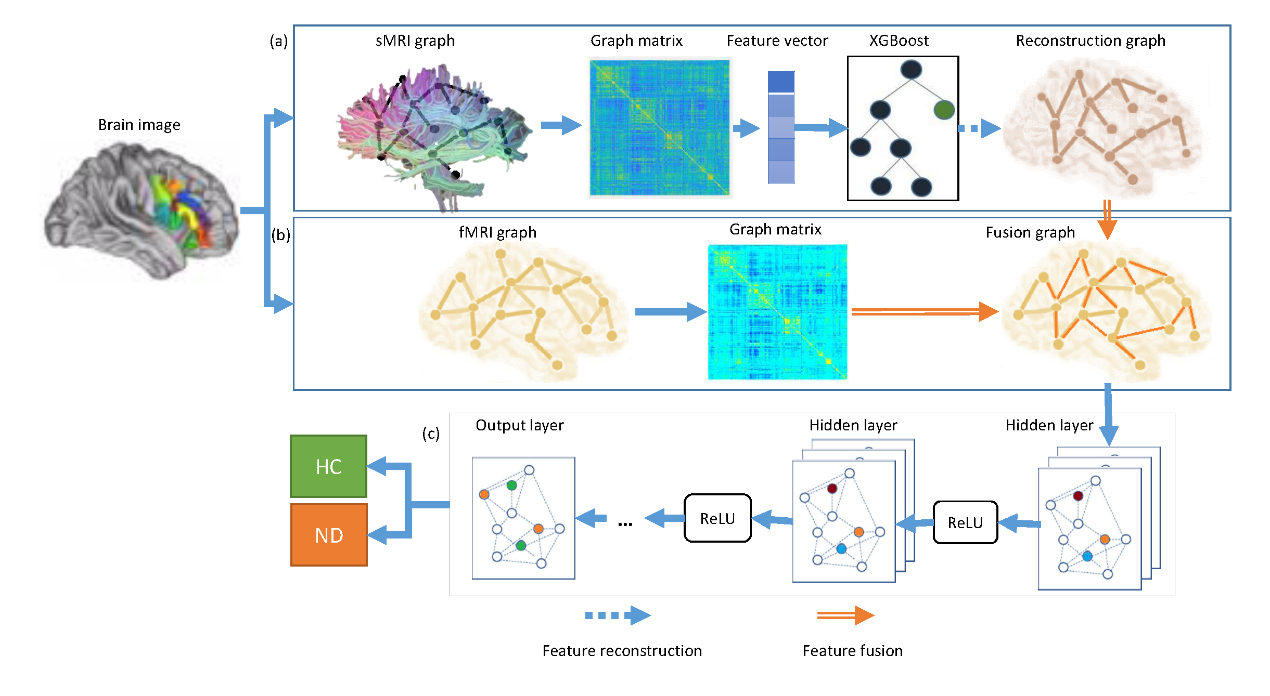
Figure1 Illustration of the proposed MME-GCN method
Furthermore, this study conducted an in-depth analysis of NDS diseases. The visualization experiment shows that the multi-modal enhancement scheme increased the weight of the network between important brain regions. In addition, this study found that ND diseases may cause asymmetry in the functional connections of the left and right hemispheres (Figure 2). This means that NDs not only involves much brain regions and connections between different hemispheres, but also has a greater impact on the functional connections of the whole brain than that within a hemisphere. These findings provide new ideas for the research of ND disease, and also provide technical support for precision treatment.
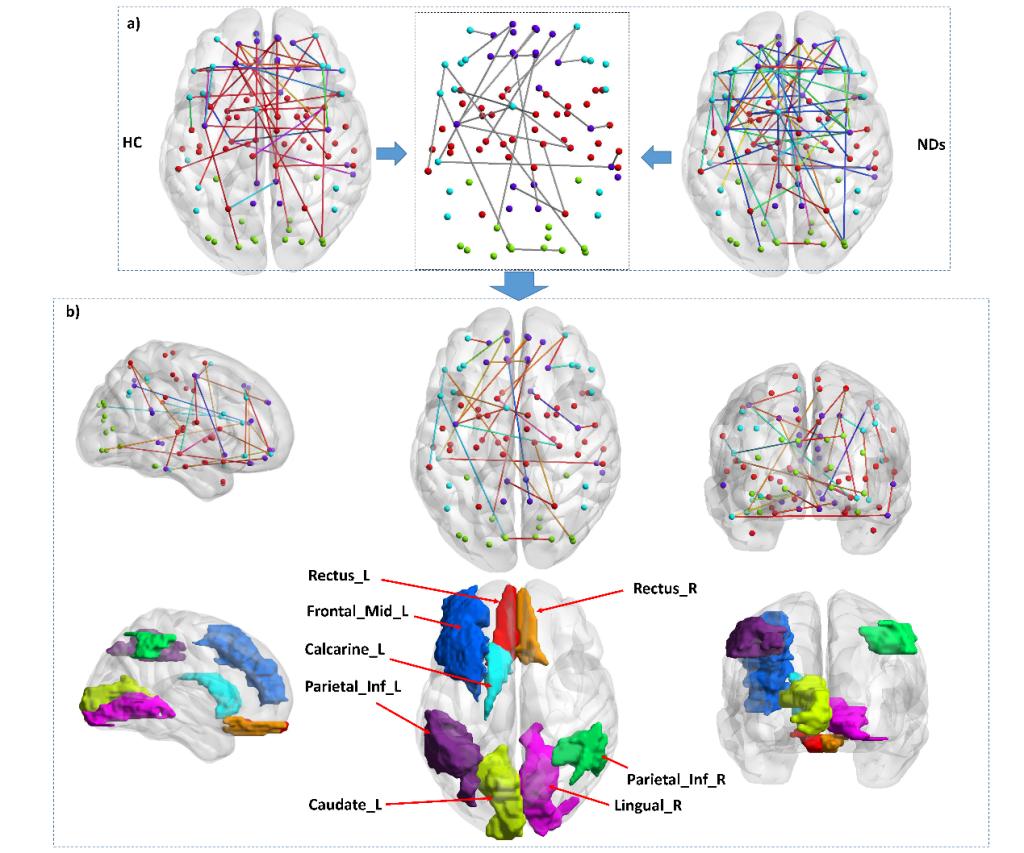
Figure 2 Connections in deep brain connectome
This achievement was published in the top medical image journal《Medical Image Analysis》 entitled "An enhanced multi modal brain graph network for classifying neuropsychiatric disorders". Liangliang Liu is the first author and corresponding author. At the same time, Professor Yu-ping Wang of Tulane University in the United States gave professional guidance.
Paper online:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2022.102550
Edited by Chen Xi
Authorized by Wang Hongyan, Zhou Hongfei






